- General Methodologies for Intelligence Analysis
- Analytical Judgments and Estimative Analysis
- Models of Intrusion and Attack Analysis
- Processes and Frameworks Supporting Threat Intelligence Analysis
General Methodologies for Intelligence Analysis
This page brings together a set of key methodologies, frameworks, and references that support intelligence analysis.
They provide practical tools for analysts, help mitigate cognitive bias, and introduce structured models for intrusion and attack analysis.
Whenever possible, these methodologies are also mapped to MISP taxonomies to enable direct application in threat intelligence platforms.
At a Glance
| Category | Methodology / Reference | Key Focus | MISP Integration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cognitive & Analytical Bias | Psychology of Intelligence Analysis (Heuer) | Understanding and mitigating cognitive biases |
confidence-in-analytic-judgment in estimative-language
|
| Judgment under Uncertainty (Tversky & Kahneman) | Heuristics and biases in uncertainty | event-assessment |
|
| Source Reliability & Confidence | Admiralty Scale | Source reliability & information credibility | admiralty-scale |
| Words of Estimative Probability | Standardized probability terms | estimative-language |
|
| JP 2-0 Appendix A | Expressing confidence in analytic judgments | estimative-language |
|
| Intrusion & Attack Models | Cyber Threat Framework | Consistent classification of cyber threats | cyber-threat-framework |
| Diamond Model | Event-centric intrusion analysis | diamond-model |
|
| Kill Chain | Intrusion phases & campaign linkage | kill-chain |
|
| MITRE ATT&CK | Tactics & techniques knowledge base | MISP Galaxy | |
| Process & Data Science Approaches | CSAE Framework | Data science for intelligence analysis | — |
Psychology of Intelligence Analysis (Richard J. Heuer, Jr.)
Psychology of Intelligence Analysis (PDF) · EPUB
This classic book provides insights for intelligence analysts, practitioners, and academics to improve analysis by understanding cognitive limitations and biases.
Analytical Judgments and Estimative Analysis
Judgment under Uncertainty: Heuristics and Biases (Amos Tversky & Daniel Kahneman)
Judgment under Uncertainty: Heuristics and Biases introduces the concept of cognitive biases that affect judgments, particularly when evaluating uncertainty — a critical concern for intelligence analysts.
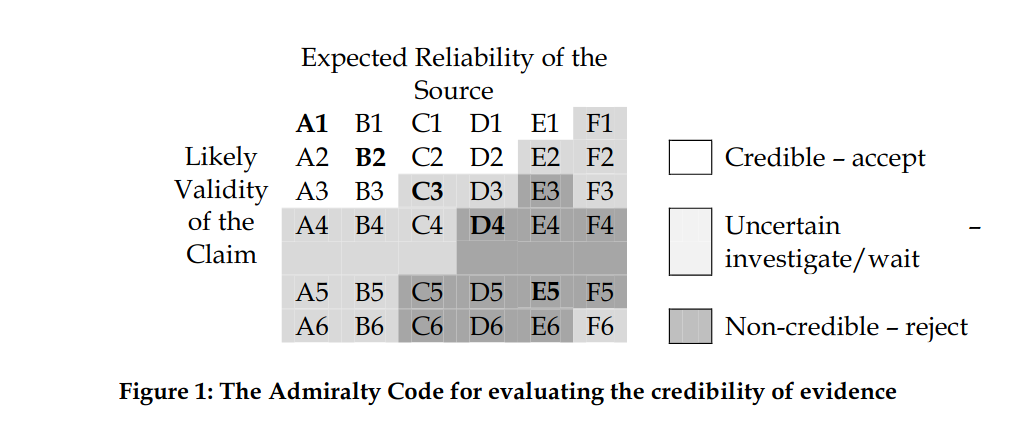
The Admiralty Scale (NATO System)
The Admiralty Scale (also known as the NATO System) ranks the reliability of sources and the credibility of information.
“The Admiralty Code is a relatively simple scheme for categorising evidence according to its credibility. It was initially used by the British Admiralty for naval intelligence, but is now applied in police departments, intelligence agencies, and defense organisations worldwide, including the US Army.”
— Ref: The Admiralty Code: A Cognitive Tool for Self-Directed Learning
- A MISP taxonomy called admiralty-scale provides a practical implementation for tagging information in a threat intelligence platform.
Words of Estimative Probability
Words of Estimative Probability proposes standardized terminology for expressing probability in analytic judgments.
- A MISP taxonomy called estimative-language provides a practical model to apply this in a structured way.
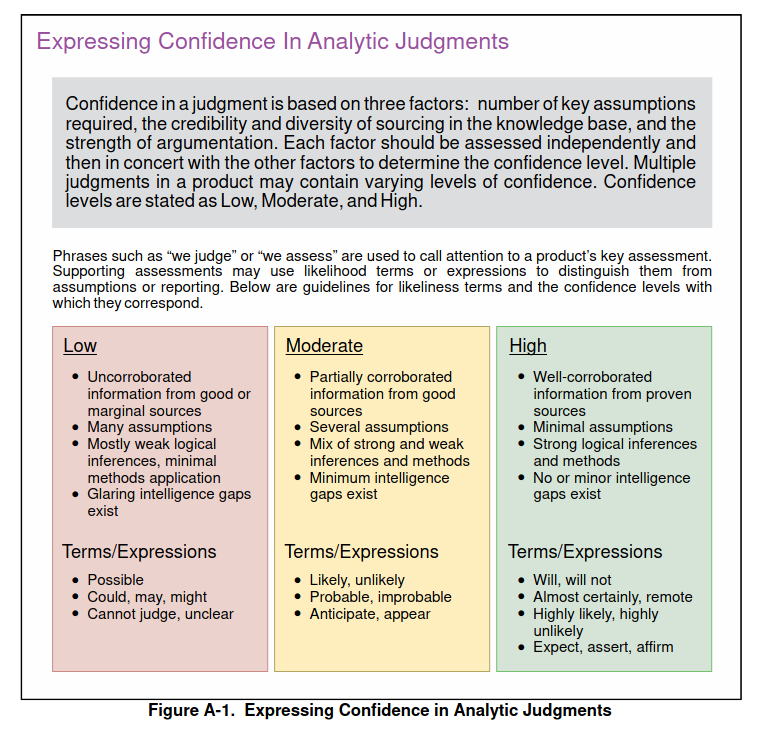
Expressing Confidence in Analytic Judgments
The US JP 2-0 Joint Intelligence (Appendix A, p.114) includes a structured method to express confidence levels in analytic judgments.
- This has been implemented in the MISP taxonomy estimative-language, enabling analysts to directly tag confidence levels on shared information.
Models of Intrusion and Attack Analysis
Cyber Threat Framework (Office of the Director of National Intelligence)
The Cyber Threat Framework was developed by the US Government to provide consistent characterization and categorization of cyber threat events. It introduces a common lexicon that supports information sharing, trend analysis, and communication between technical analysts and policymakers.
— Ref: Cyber Threat Framework
- Implemented as a MISP taxonomy.
The Diamond Model of Intrusion Analysis
The Diamond Model of Intrusion Analysis (Sergio Caltagirone, Andrew Pendergast, Christopher Betz) establishes the event as the atomic element of intrusion analysis, defined by four features: adversary, infrastructure, capability, and victim.
- Implemented as a MISP taxonomy.
Intelligence-Driven Computer Network Defense (Kill Chain Model)
Intelligence-Driven Computer Network Defense Informed by Analysis of Adversary Campaigns and Intrusion Kill Chains (Eric M. Hutchins, Michael J. Cloppert, Rohan M. Amin) introduces the kill chain model.
This model maps phases of adversary intrusions to defender actions, linking individual intrusions into campaigns.
- Implemented as a MISP taxonomy.
MITRE ATT&CK
MITRE ATT&CK™ is a curated knowledge base and framework of adversary tactics and techniques, reflecting phases of adversary lifecycles and targeted platforms.
It is widely used to:
- Assess security risks based on known adversary behavior
- Plan and prioritize defensive improvements
-
Validate the effectiveness of security controls
- MISP includes the full ATT&CK dataset as a galaxy also easily searchable at https://misp-galaxy.org/.
Processes and Frameworks Supporting Threat Intelligence Analysis
CSAE Framework — Collect, Store, Analyze, Engage
A Comprehensive Data Science Framework and Case Study for Investigating Organized Crime and Serving the Public Interest
Erik van de Sandt, Arthur van Bunningen, Jarmo van Lenthe, John Fokker
This framework (CSAE) applies data science methodologies to intelligence work, with a particular case study in organized crime investigations, illustrating how to collect, store, analyze, and engage with intelligence effectively.